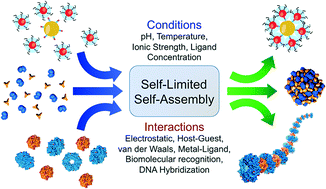
Nanotechnology utilizes various techniques to fabricate nanoscale structures and devices. Bottom-up techniques, in particular, involve the assembly of individual atoms, molecules, or nanoparticles to build larger structures. Self-assembly is a prominent bottom-up technique in which components spontaneously organize themselves into ordered structures. Here are the steps involved in self-assembly, along with their application, advantages, and disadvantages:
Steps in Self-Assembly:
1. Component Design: Designing and synthesizing individual components, such as nanoparticles or molecules, with specific properties and functionalities.
2. Interaction Design: Designing the components to possess complementary interactions, such as electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding, or hydrophobic interactions, to facilitate self-assembly.
3. Assembly Process: Providing appropriate conditions (e.g., temperature, solvent, pH) for the components to interact and assemble into the desired structure.
4. Structure Characterization: Analyzing the resulting structures using techniques like microscopy, spectroscopy, or diffraction to verify the desired assembly.
Application of Self-Assembly:
Self-assembly has a wide range of applications across various fields, including:
1. Nanoelectronics: Self-assembly can be used to fabricate nanoscale electronic devices and circuits with high precision and density.
2. Drug Delivery Systems: Self-assembled nanocarriers can encapsulate and deliver drugs to targeted sites in the body, improving therapeutic efficiency and reducing side effects.
3. Surface Coatings: Self-assembled monolayers can be employed to modify surfaces, providing functionalities such as increased hydrophobicity, biocompatibility, or corrosion resistance.
4. Photonic Devices: Self-assembled nanostructures can be utilized to fabricate photonic devices, such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or photovoltaic cells, with enhanced performance.
Advantages of Self-Assembly:
1. Scalability: Self-assembly techniques can potentially produce large quantities of ordered structures with minimal effort.
2. Cost-Effectiveness: Self-assembly can reduce fabrication costs by minimizing the need for complex manufacturing processes.
3. Precision and Complexity: Self-assembly allows for the creation of intricate structures at the nanoscale, which may be challenging to achieve through traditional top-down approaches.
Disadvantages of Self-Assembly:
1. Lack of Control: Achieving the desired structure through self-assembly may sometimes be challenging, as the process relies on the inherent properties of the components and their interactions.
2. Limited Materials: Self-assembly techniques may be limited to specific types of materials that can effectively interact and assemble.
3. Reproducibility: Ensuring the reproducibility of self-assembly processes can be difficult, as small variations in conditions or component properties may lead to different outcomes.
মন্তব্যসমূহ
একটি মন্তব্য পোস্ট করুন