Soft lithography is a set of techniques used for patterning and replicating structures on the micro- and nanoscale. It involves the use of elastomeric materials, such as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), to create molds or stamps that can transfer patterns onto different substrates.
1. Design and fabrication of the master mold: The desired pattern is first designed using computer-aided design (CAD) software. Then, the master mold is fabricated using techniques like photolithography, electron beam lithography, or nanoimprint lithography. The master mold contains the negative replica of the desired pattern.
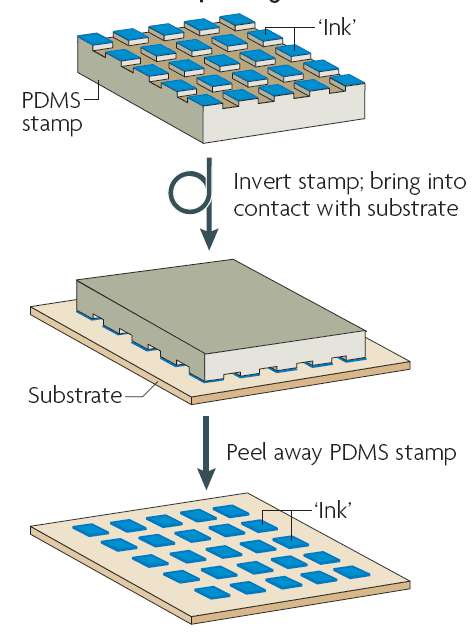
2. Preparation of the elastomeric stamp: A liquid elastomer, typically PDMS, is mixed with a curing agent and poured onto the master mold. After curing, the PDMS replica of the master mold is obtained. The PDMS stamp contains the positive replica of the desired pattern.
3. Surface treatment: The surface of the PDMS stamp is treated to make it adhesive or non-adhesive depending on the application. This treatment can involve oxygen plasma treatment, chemical modification, or coating with a self-assembled monolayer.
4. Pattern transfer: The treated PDMS stamp is brought into contact with the substrate material, such as a thin film or a nanomaterial precursor solution. The stamp is gently pressed against the substrate to ensure good contact and pattern transfer.
5. Demolding and curing: After pattern transfer, the PDMS stamp is carefully removed from the substrate. If necessary, the patterned substrate is cured to fix the pattern in place. Curing can involve thermal or UV treatment, depending on the material used.
6. Post-processing steps: Additional steps such as etching, deposition, or annealing may be performed to further modify the patterned substrate and achieve the desired properties.
Applications of soft lithography in nanomaterials synthesis:
1. Fabrication of microfluidic devices
2. Nanopatterning for electronic devices
3. Biomaterial engineering
Advantages of soft lithography for nanomaterials synthesis:
1. Low-cost and accessible
2. Versatility
3. Scalability
Disadvantages of soft lithography for nanomaterials synthesis:
1. Resolution limitations: The resolution of soft lithography techniques is typically lower compared to more advanced lithography methods like electron beam lithography, which may limit the achievable feature sizes and densities.
2. Material compatibility: Soft lithography may not be suitable for all types of materials, as some materials may not adhere well to the PDMS stamp or may interact unfavorably with the stamp during the patterning process.
3. Complexity of mold fabrication: Fabricating the master mold for soft lithography can be a complex and time-consuming process, particularly for intricate patterns or high-resolution features.
মন্তব্যসমূহ
একটি মন্তব্য পোস্ট করুন